Accidentally short-circuiting your car’s fuse box can be a frustrating experience, often leading to a no-start situation. If you’ve ever had a tool slip while working under the hood, and witnessed that dreaded spark near your car’s fuse box, you might be facing a similar issue. This guide will walk you through the initial steps to diagnose and potentially resolve the problem, focusing on the crucial role of the fuse box and related components.
Understanding the Incident: The Fuse Box Short Circuit
As seen in a recent forum discussion, a user encountered a no-start issue after accidentally arcing a tool on the main power lead of their car’s fuse box. This common mishap highlights the vulnerability of the fuse box area, especially when working with tools and exposed terminals. The immediate consequence is often a blown fuse, but it can sometimes lead to more complex electrical problems.
Initial Troubleshooting Steps
If your car fails to start after a similar incident, here are the first steps you should take:
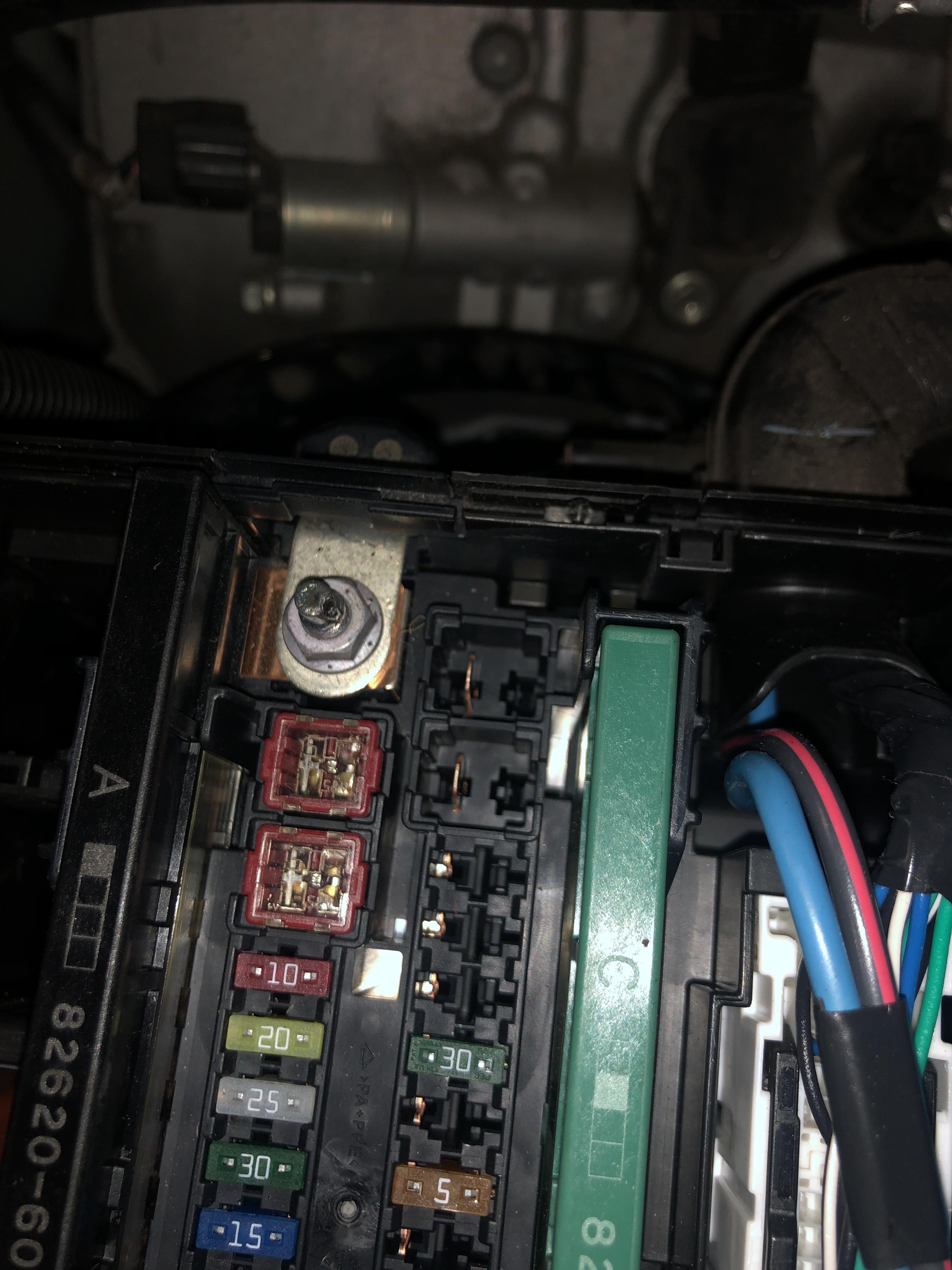
1. Fuse Inspection: The First Line of Defense
Your car’s fuse box is designed to protect the electrical system from overloads. The first and most logical step is to check the fuses within the fuse box. Refer to your car’s owner’s manual for the fuse box location (typically under the hood and sometimes under the dashboard) and the fuse diagram.
- Visual Inspection: Look for blown fuses – they usually have a broken filament inside.
- Fuse Tester: Use a fuse tester tool for a more reliable check. This tool quickly indicates whether a fuse is still functional.
- Replacement: Even if a fuse looks intact, try replacing fuses related to the starting system and main power, especially if you suspect they were near the arcing point. Keep spare fuses of the correct amperage in your car for such situations.
2. Battery Reset: A Simple Solution
Sometimes, an electrical surge can confuse the car’s computer system. A simple battery reset can often resolve minor electrical glitches.
- Disconnect Negative Terminal: Locate the negative terminal of your car battery (usually marked with a ‘-‘ sign or black color). Use a wrench to loosen the nut and disconnect the cable.
- Wait: Let the car sit for about 5-10 minutes. This allows the electrical system to fully discharge and reset.
- Reconnect: Reconnect the negative battery cable and tighten the nut securely.
- Test Start: Try starting your car again.
Deeper Investigation if Initial Steps Fail
If checking fuses and resetting the battery doesn’t solve the problem, the issue might be more intricate. Consider these further checks:
1. Fusible Links and Main Fuses
Some vehicles, especially older models, use fusible links – heavy-duty fuses often located near the battery or under the main fuse box. These are designed to protect major circuits.
- Location: Check near the battery positive terminal and underneath the main fuse box for larger fuses or fusible links.
- Inspection: Inspect for any signs of melting or damage. These may require more effort to access and replace.
2. Relays
Relays are electrical switches that control various circuits in your car. An electrical arc can damage relays.
- Location: Relays are also typically found in the fuse box. Consult your car’s diagram to identify relays related to the starting system.
- Testing: You can try swapping relays with identical ones (if available and if you know they are functional) to see if it resolves the issue. Alternatively, a multimeter can be used to test relay functionality.
3. Potential Component Damage
While less common with a brief arc, it’s possible that sensitive electronic components could be damaged by a power surge. If you’ve exhausted the fuse and relay checks, further professional diagnosis might be necessary.
Prevention is Key: Using the Right Tools and Precautions
To prevent such incidents in the future, always take these precautions:
- Disconnect Battery: Before working on any electrical components, especially around the fuse box, disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Use Insulated Tools: When working near the fuse box or any electrical terminals, use insulated tools to minimize the risk of short circuits.
- Fuse Box Cover Tool: A specialized Car Fuse Box Cover Tool can be incredibly helpful. These tools are designed to safely and easily remove and install fuse box covers, often incorporating fuse pullers and minimizing the chances of accidental shorts while accessing the fuse box. Using the right tool ensures you can access fuses without fumbling with screwdrivers or other metallic objects that could cause shorts.
Conclusion: Proceed with Caution and the Right Tools
Dealing with car electrical issues after a fuse box mishap can be daunting. Start with the basics: check your fuses and try a battery reset. If the problem persists, systematically investigate fusible links and relays. Remember, safety is paramount. Using appropriate tools like a car fuse box cover tool and disconnecting the battery during electrical work can significantly reduce the risk of accidental short circuits and keep your car maintenance tasks safer and more efficient. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with these steps, seeking professional help from a qualified mechanic is always the best course of action.