Home health care agencies (HHAs) face unique challenges in ensuring quality care and patient safety. Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) programs, mandated by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), provide a structured framework for continuous improvement. This article explores the essential QAPI tools and strategies for HHAs to enhance care delivery and meet regulatory requirements.
QAPI is not merely a regulatory burden; it’s a proactive approach to elevating the standard of care provided in patients’ homes. By embracing data-driven methodologies and continuous improvement strategies, HHAs can optimize operational efficiency and enhance patient outcomes.
Understanding QAPI in Home Health Care
QAPI is a data-driven, proactive approach to improving the quality of care and services in HHAs. It operates under the Medicare Part A benefit, focusing on part-time, medically necessary skilled care like nursing, physical therapy, and speech therapy. The core components of QAPI are:
- Quality Assurance (QA): Systematic data collection and evaluation to monitor care outcomes and ensure compliance with established standards and regulations.
- Performance Improvement (PI): Focuses on improving processes and systems within the agency to enhance care quality and patient outcomes. This involves identifying areas for improvement, implementing changes, and measuring their effectiveness.
QAPI programs require comprehensive participation from all levels of the HHA, from management to frontline staff. Clear objectives, data-driven decision-making, and analysis of patient outcomes, satisfaction, and operational efficiency are crucial for success.
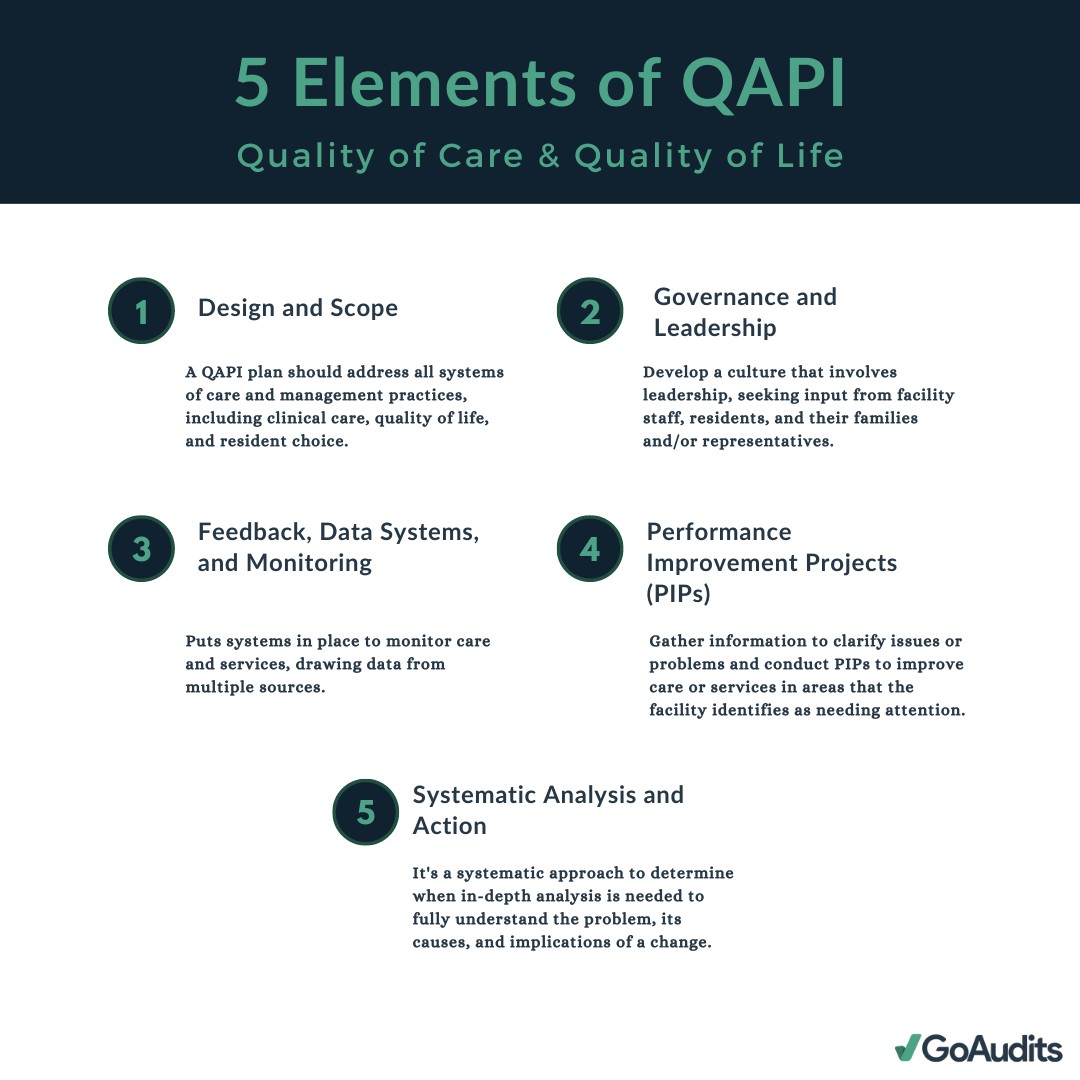
Implementing a QAPI Plan: Key Elements
CMS outlines five core elements for effective QAPI programs in HHAs:
1. Design and Scope
The QAPI program must demonstrate measurable improvements in indicators linked to enhanced health outcomes, patient safety, and quality of care. HHAs must measure, analyze, and track quality indicators, including adverse patient events.
2. Governance and Leadership
The governing body of the HHA holds ultimate responsibility for the QAPI program. This includes defining, implementing, and maintaining the program; prioritizing quality and patient safety; and addressing fraud or waste.
3. Feedback, Data Systems, and Monitoring
Utilizing quality indicator data from sources like the Outcome and Assessment Information Set (OASIS) is crucial. Data must be used to monitor service safety and quality, identify improvement opportunities, and ensure safe care delivery.
4. Performance Improvement Projects (PIPs)
HHAs must conduct annual improvement projects reflecting the scope, complexity, and past performance of their services. Thorough documentation of these projects is essential.
5. Systematic Analysis and Action
Performance improvement activities should target high-risk, high-volume, or problem-prone areas. This includes tracking and analyzing adverse patient events and implementing preventive actions. Sustained improvements should be tracked and measured.
Utilizing QAPI Tools and Resources
Several resources are available to assist HHAs in implementing effective QAPI programs:
- Home Health Value-Based Purchasing (HHVBP) Model: Incentivizes quality improvement by adjusting payments based on care quality.
- Home Health Conditions of Participation (CoPs): Outline specific QAPI requirements for HHAs.
- Healthcare Auditing Software: Streamlines data collection, documentation, and reporting for QAPI programs. Examples include mobile auditing apps and customizable checklists.
Overcoming Challenges in Home Health Care Quality
HHAs face unique challenges impacting quality, including:
- Staffing Shortages: High turnover rates necessitate robust training and retention strategies.
- Ensuring Patient Safety in the Home Setting: Requires comprehensive training programs and the adoption of technology for better care management.
- Patient Engagement and Education: Crucial for successful outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions.
- Care Coordination: Effective communication with other healthcare providers is essential for continuity of care.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex regulations requires ongoing education and meticulous documentation.
Benefits of a Robust QAPI Program
Implementing a strong QAPI program yields significant benefits:
- Improved Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction
- Cost Reduction through Efficiency
- Increased Regulatory Compliance
- Potential for Enhanced Reimbursement
- Data-Driven Decision Making
- Proactive Risk Management
- Improved Communication and Collaboration
By embracing QAPI principles and utilizing available tools, HHAs can significantly enhance the quality of care delivered in the home setting, improve patient outcomes, and strengthen their overall operational efficiency. A commitment to continuous improvement through QAPI is an investment in the future of home health care.